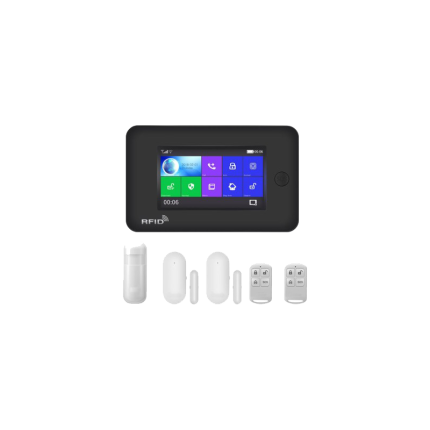
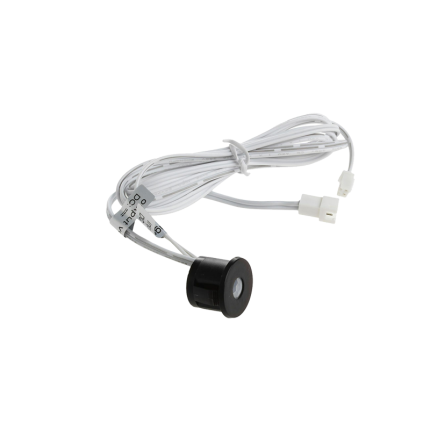
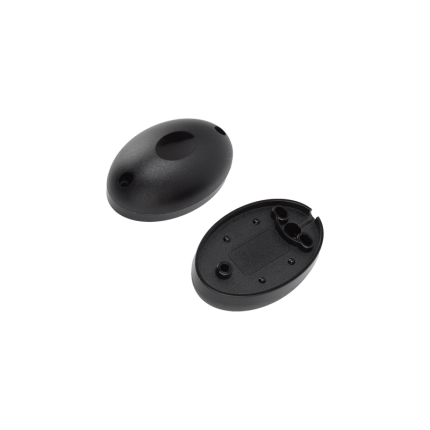
PIR Infrared Sensor – wired
*DC 12 V
*NC/NO
The PIR infrared sensor is commonly used in motion detectors, security alarms, and automatic lighting systems. PIR infrared sensors are “passive” because they don’t emit any energy themselves; they detect changes in infrared radiation emitted by objects, like humans or animals, as they move.
-
How PIR infrared sensor works:
PIR infrared sensors have two slots made of a special infrared-sensitive material. When a warm object, like a person, moves into the sensor’s field of view, it interrupts the infrared radiation detected by one slot more than the other, causing a “change” that triggers the sensor.
-
Applications:
- Security: Detecting intruders in alarm systems.
- Lighting: Automatically turning lights on when someone enters a room or area.
- Energy Management: Optimizing energy consumption by controlling devices based on occupancy.
- Industrial Monitoring: Detecting the movement of machinery or equipment.
- Wildlife Tracking: Monitoring animal movements without direct human observation.
- Security: Detecting intruders in alarm systems.
-
Advantages:
- Low power consumption: They require very little energy to operate.
- Cost-effective: They are relatively inexpensive to manufacture and use.
- Easy to integrate: They are simple to incorporate into various systems and devices.
- Privacy protection: They only detect heat signatures and don’t collect detailed visual information.
- Low power consumption: They require very little energy to operate.
-
Limitations:
- False triggers: Can be triggered by rapid temperature changes, drafts, or moving objects.
- Not as reliable as active sensors: They may not detect slow-moving or small objects as effectively as active sensors.
- Limited range: The PIR infrared sensor have a limited range of detection compared to other sensor types.
- False triggers: Can be triggered by rapid temperature changes, drafts, or moving objects.


























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.