Ship or pick up from our office.
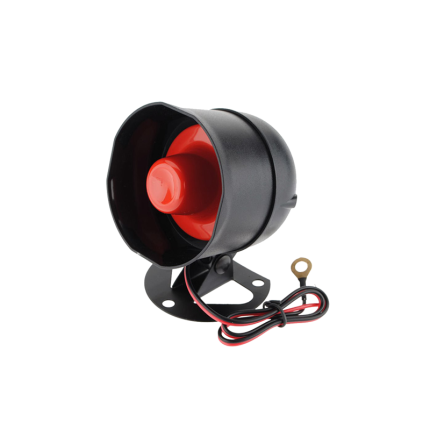
Siren
A
siren is a noise-making warning device designed to produce a loud, often piercing or fluctuating sound to alert people to an emergency, an approaching threat, or to draw attention to a specific situation.
Sirens are characterized by their ability to generate high sound pressure levels (decibels) that can be heard over long distances and through various obstacles.
There are two main types of sirens:
- Mechanical (or Pneumatic) Sirens:
- How they work: These sirens produce sound by physically chopping or interrupting a flow of air. They typically consist of a rotating disk (rotor) with holes or slots, which spins rapidly past fixed holes or slots on a stationary casing (stator). As the rotor spins, it alternately allows and blocks air to pass through, creating pulsating air pressure waves that we perceive as sound. The pitch of the siren changes with the speed of the rotor and the number of holes.
- Characteristics: Often produce a characteristic "wailing" or "growling" sound. They can be very loud and consume significant power.
- Uses: Traditionally used as large outdoor warning sirens (e.g., air-raid sirens, tornado sirens) and on older emergency vehicles. You might still hear them in some older industrial settings as well.
- Electronic Sirens:
- How they work: These are the most common type found in modern applications. They generate sound electronically using circuits like oscillators, modulators, and amplifiers. These circuits synthesize various siren tones, which are then played through powerful external speakers.
- Characteristics: Highly versatile, able to produce a wide range of distinct tones (e.g., Wail, Yelp, Phaser/Piercer, Hi-Lo, Air Horn, Manual), and can often include voice announcements. They are generally more compact, consume less power than large mechanical sirens, and are easier to control.
- Uses:
- Emergency Vehicles: Police cars, ambulances, fire engines, and other emergency response vehicles use electronic sirens to alert traffic and pedestrians to their presence and urgency. Different tones are often used for different situations (e.g., Wail for distant approach, Yelp for closer proximity or heavy traffic, Air Horn for immediate attention).
- Vehicle Alarms: Car alarms commonly use a smaller, electronic siren (or the vehicle's horn) to sound a loud alert when triggered by a sensor (like a shock sensor, door sensor, or ultrasonic sensor).
- Security Systems: Residential and commercial alarm systems use sirens to deter intruders and alert occupants and neighbors to a security breach.
- Industrial and Safety Alarms: Used in factories, construction sites, and other workplaces to signal shift changes, emergencies, or specific warnings.
- Civil Defense/Public Warning Systems: Modern outdoor warning systems often use large electronic sirens that can broadcast specific tones and even pre-recorded voice messages for events like severe weather, hazardous material spills, or other public safety alerts.
In the context of vehicle alarms (which you asked about previously):
When discussing a car alarm, the "siren" specifically refers to the dedicated, loud sound-emitting device that is activated when the alarm system is triggered. This siren is almost always an electronic type, designed to create a very piercing and attention-grabbing sound to deter thieves and alert the vehicle owner and those nearby. It's distinct from the vehicle's regular horn, although some simpler alarm systems might just use the car's horn.




















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.