driveway gates
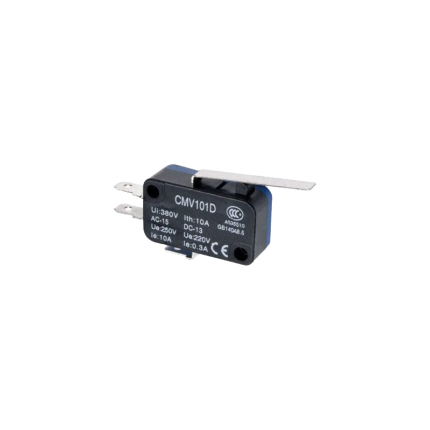
Micro Limit Switch
Ship or pick up from our office.
Micro Limit Switch
A micro limit switch, often simply called a micro switch, is a type of electrical switch that's characterized by its small size and the precise, rapid action it takes when a minimal amount of force is applied to its actuator. It's designed to detect the presence or position of an object or the end of a mechanical movement. These switches are known for their:- High sensitivity: They require very little force to activate.
- Rapid response: The internal contacts "snap" open or closed very quickly, regardless of how slowly the actuator is pressed. This snap-action mechanism helps to reduce arcing and extends the switch's lifespan.
- Reliability: They are built to withstand millions of operations, making them durable for long-term use.
- Compact size: Their small footprint allows them to be used in applications where space is limited.
- Actuator: This is the external part that an object or mechanical component presses against. It can be a button, a lever (with or without a roller), a plunger, or other forms.
- Internal spring mechanism: This provides the "snap-action." When the actuator is pressed to a certain point (the "trip point"), the spring mechanism rapidly moves the contacts.
- Contacts: These are the electrical components that open or close the circuit. Micro switches usually have three terminals:
- Common (C): The input terminal.
- Normally Open (NO): This contact is open (no current flows) when the switch is unactivated and closes when the switch is actuated.
- Normally Closed (NC): This contact is closed (current flows) when the switch is unactivated and opens when the switch is actuated
- Household Appliances:
- Microwave ovens: To detect if the door is closed before operating.
- Washing machines: For door interlocks and water level detection.
- Refrigerators: To turn the light on/off when the door opens/closes.
- Printers: To detect paper jams or the position of paper.
- Automotive Industry:
- Car doors: To detect if a door is open or closed (e.g., for interior lights or security systems).
- Brake pedals: To activate brake lights.
- Seat belt mechanisms: To detect if a seat belt is fastened.
- Industrial Automation:
- Conveyor systems: To detect the presence of items or the end of travel for a belt.
- Robotic arms: For precise positioning and limit detection of movement.
- Machine safety guards: To ensure guards are correctly positioned before machinery operates.
- Elevators and hoists: To prevent over-travel and ensure proper door operation.
- Consumer Electronics:
- Computer mice and keyboards: For button clicks.
- Vending machines: For coin detection or jam detection.
- Medical Equipment:
- In various diagnostic tools and surgical instruments for precise control.
- Pin Plunger: A simple button-like plunger that is directly pressed.
- Roller Lever: Features a lever with a roller at the end, ideal for applications with sliding or rotating components.
- Hinge Lever: A simple lever arm that pivots to actuate the switch.
- Flexible Roller: Similar to a roller lever, but with a more flexible arm to accommodate irregular surfaces or wider ranges of motion.
- Spring Plunger: A plunger supported by a spring, allowing for a certain degree of "overtravel" beyond the actuation point without damaging the switch.
Programmer module -Key Automation KUBEPRO
Ship or pick up from our office.
PRODUCT SHEET PDFProgrammer module -Key Automation KUBEPRO
*KUBEPRO - Installer Version *Smartphone programming for 14A and HALO control boardsThe Key Automation KUBEPRO is a programmer module that allows professional installers to configure and manage Key Automation gate and door operators using a smartphone.
It connects via Bluetooth to the installer's smartphone and allows them to adjust parameters, set up the gate opener, and manage other aspects of the automation system.
The KUBE PRO also includes the KEY CLOUD service for data viewing, backup, team management, and maintenance scheduling.
Here's a more detailed breakdown:
-
Purpose:The KUBEPRO is designed for professional installers to configure and manage Key Automation gate and door operators.
-
Functionality:It allows installers to adjust various parameters, set up the gate opener, and manage other settings directly from their smartphone.
-
Connectivity:It connects to the gate operator's control board and uses Bluetooth to communicate with the installer's smartphone.
-
Smartphone App:An app, specifically designed for professional installers, is used to interact with the KUBEPRO module.
-
KEY CLOUD:The KUBE PRO module includes KEY CLOUD, a cloud-based service for storing data, managing teams, and scheduling maintenance.
-
Accessibility:The KUBE PRO module is restricted to users with a Key Automation account, ensuring proper authorization and usage.
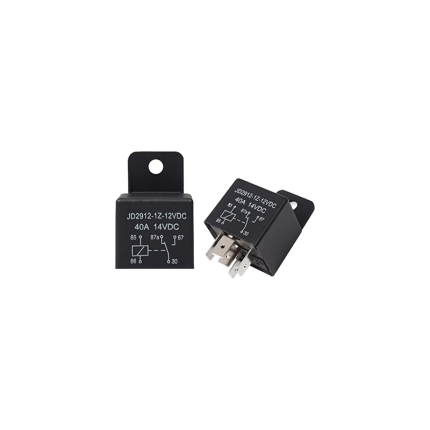
Relay 5-Pin 40A
Ship or pick up from our office.
Relay 5-Pin 40A
A 5-pin 40A relay is an electromechanical switch commonly used in automotive and other applications. It allows a low-power electrical signal to control a higher-power circuit. The "5-pin" refers to the number of terminals it has, and "40A" indicates that its contacts can safely handle a maximum current of 40 amps. How it Works A relay essentially functions like a remote-controlled switch. It has two main circuits:- Control Circuit (Coil): This low-power circuit energizes an electromagnet inside the relay.
- Switched Circuit (Contacts): This high-power circuit is controlled by the electromagnet, either opening or closing connections to a device.
- Pins 85 and 86: These are the coil terminals. When a small current (typically 12V DC in automotive applications) is applied across these pins, it creates a magnetic field.
- Pin 30: This is the common terminal for the switched circuit. It's usually connected to the main power source (e.g., battery) through a fuse.
- Pin 87: This is the Normally Open (NO) contact. When the relay coil is energized, pin 30 connects to pin 87, allowing current to flow to the connected device.
- Pin 87a: This is the Normally Closed (NC) contact. When the relay coil is not energized, pin 30 is connected to pin 87a. When the coil is energized, this connection breaks.
- High-Current Control: They allow you to control high-current devices (like headlights, fuel pumps, or cooling fans) with a low-current switch. This protects the sensitive, smaller switches from being damaged by excessive current.
- Reduced Voltage Drop: By placing the relay closer to the high-current device and power source, you can use shorter runs of heavier gauge wire for the high-current circuit, minimizing voltage drop and ensuring the device receives adequate power.
- Safety: They isolate high-current circuits from the passenger compartment, enhancing safety.
- Automotive: Headlights, fog lights, horns, fuel pumps, electric cooling fans, power windows, central locking, and various aftermarket accessories.
- Industrial Control: Switching motors, solenoids, and other heavy-duty equipment.
- General Purpose: Any application where a low-power signal needs to control a higher-power circuit.
- Pin 85: Connect to ground (-).
- Pin 86: Connect to the positive (+) side of your control switch. When this switch is activated, it provides power to the coil.
- Pin 30: Connect directly to the positive (+) terminal of your battery, always through an appropriately sized fuse.
- Pin 87: Connect to the positive (+) terminal of the device you want to power when the relay is activated (Normally Open connection).
- Pin 87a: (Optional) Connect to a device you want to power when the relay is not activated (Normally Closed connection).
Relay Mini PCB 5-Pin 10A
Ship or pick up from our office.
Relay Mini PCB 5-Pin 10A
A Relay Mini PCB 5-Pin 10A is a compact, electromechanical switch designed to be mounted directly onto a printed circuit board (PCB). It uses a small control voltage to switch a larger current, making it useful for isolating control circuits from power circuits or for switching higher-power loads with a low-power signal. Key Features and Specifications- Mini: This indicates its small physical size, making it suitable for applications where space is limited.
- PCB: This means it's designed for Printed Circuit Board mounting. Its pins are typically configured to be soldered directly into holes on the PCB.
- 5-Pin: These five pins usually consist of:
- Two pins for the coil: These are where the control voltage is applied to energize the coil and activate the relay.
- Three pins for the contacts: These typically include a common (COM) pin, a normally open (NO) pin, and a normally closed (NC) pin.
- 10A: This is the maximum current rating that the relay's contacts can safely switch. It means the relay is capable of handling up to 10 amperes of current through its switched contacts.
- Normally Open (NO): The contact is open when the coil is de-energized and closes when the coil is energized.
- Normally Closed (NC): The contact is closed when the coil is de-energized and opens when the coil is energized.
- Automotive applications: For controlling lights, motors, and other accessories.
- Home automation: Switching lights, appliances, and HVAC systems.
- Industrial control: In PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) and other control panels.
- Appliance control: In washing machines, refrigerators, and microwave ovens.
- DIY electronics projects: Where low-power signals need to control higher-power devices.
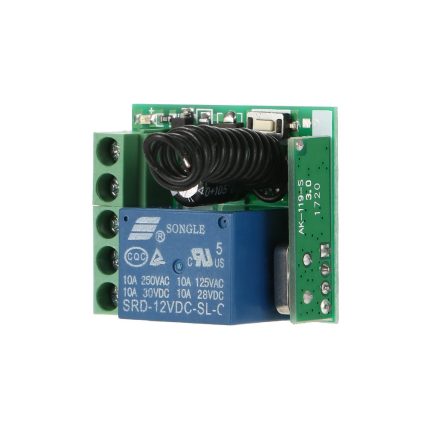
Remote Control Radio Receiver
Ship or pick up from our office.
Remote Control Radio Receiver
- NC/NO Output
- Easy to program new remotes
- The remote control button is covered to prevent accidental pressing.
- This radio receiver can be added to almost all the gate operators such as Italian, Chinese, swing gate operators, sliding gate operators, and overhead garage doors.
- Compatible with 100 remotes.
- Small case and easy to install
- The wireless RF signals can pass through walls, floors, doors, or windows. You can use two or more units in the same place.
A gate opener's remote control radio receiver is a device that receives radio signals from a handheld remote control, triggering the gate opener's motor to open or close the gate.
Here's a more detailed explanation:
-
Receives Signals:The receiver picks up radio waves transmitted by the remote control.
-
Decodes Commands:It interprets the specific signal pattern to understand the desired action (e.g., open, close, stop).
-
Controls Devices:The receiver then sends signals to the gate opener's motor, causing it to move the gate accordingly.
-
Part of a System:It's a crucial component of the remote control system, working with the transmitter (remote) to enable wireless control of the gate.
-
Frequency:Gate opener receivers typically operate on frequencies like 433 MHz or 315 MHz.
-
Installation:The receiver is usually wired to the gate operator's control board and may require programming to associate it with specific remote controls.
RFID Tag Access Control
Ship or pick up from our office.
RFID Tag Access Control
RFID Tag Access Control is a system that uses Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology to manage and control access to physical spaces or logical systems. It allows only authorized individuals or items to enter secure areas by wirelessly reading data stored on RFID tags. Think of it as a modern, electronic key system where your "key" is an RFID tag (like a card or key fob) and the "lock" is an RFID reader. How it Works ⚙️ The fundamental principle is straightforward:- RFID Tag/Credential: Each authorized individual or item is assigned an RFID tag. This tag contains a microchip that stores a unique identification code and an antenna.
- RFID Reader: A reader (also called an interrogator) is installed at the access point (e.g., a door, gate, or turnstile). The reader emits radio waves.
- Communication: When an RFID tag comes within range of the reader's radio waves, the tag's antenna captures energy from the reader's signal (for passive tags) or uses its own power source (for active tags) to activate its microchip. The tag then transmits its unique data back to the reader.
- Data Processing: The reader decodes the information from the tag and sends it to a central access control software or system.
- Authentication and Decision: The software compares the tag's unique ID with a database of authorized users and their assigned permissions. If the ID is valid and the user has permission to access that specific area at that time, the system sends a signal to unlock the door, open the gate, or grant access. If not, access is denied.
- Logging: The system typically logs every access attempt (both granted and denied), providing an audit trail for security monitoring and compliance.
- RFID Tag Access Controls/Credentials: These are the physical devices carried by users. They come in various forms, such as:
- Cards: Similar to credit cards, commonly used for employee badges or hotel key cards.
- Key Fobs: Small, convenient devices attached to keychains.
- Wristbands: Often used in recreational facilities or for events.
- Stickers/Labels: Can be affixed to items or vehicles.
- Mobile Credentials: Increasingly, smartphones can act as RFID tags through NFC (Near Field Communication), a subset of HF RFID.
- RFID Readers: Devices that emit radio waves to energize and read data from RFID tags. They can be fixed (at entry points) or mobile (handheld scanners).
- Antennas: Integral to the reader (or external), they transmit and receive radio signals to and from the tags. The antenna design influences the read range and reliability.
- Access Control Software/Management System: The "brain" of the system. This software manages user databases, assigns access permissions, logs events, and allows administrators to configure and monitor the system remotely.
- Access Control Panel/Controller: Hardware that connects the readers to the central software, processing data and controlling the locking mechanisms.
- Passive RFID Tags:
- Do not have an internal power source.
- They draw power from the radio waves emitted by the reader to operate.
- Are generally smaller, less expensive, and require no maintenance.
- Have a shorter read range (a few centimeters to a few feet).
- Most commonly used in access control for cards and key fobs.
- Active RFID Tags:
- Have their own internal power source (battery).
- Can transmit data over longer distances (up to several hundred meters) and at regular intervals.
- Are larger and more expensive.
- Often used for long-range applications like vehicle tracking or asset management.
- Semi-Passive RFID Tags (Battery-Assisted Passive - BAP):
- Contain a battery to power the microchip, but still rely on the reader's signal to initiate communication.
- Offer better read range and performance than passive tags, without continuously transmitting like active tags.
- Low Frequency (LF) RFID (125-134 kHz):
- Short read range (1-10 cm).
- Less susceptible to interference from metal and water.
- Common in traditional access control systems.
- High Frequency (HF) RFID (13.56 MHz):
- Moderate read range (10 cm-1 meter).
- Widely used for access control, ticketing, and Near Field Communication (NFC) applications (like smartphone taps).
- Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) RFID (300 MHz-3 GHz, often 860-960 MHz for RAIN RFID):
- Long read range (up to 12 meters).
- More susceptible to interference from liquids and metals.
- Used in applications requiring longer read distances, such as vehicle access control or large-scale inventory tracking.
Safety sensor VEDO180
Ship or pick up from our office.
Safety sensor VEDO180
*NO/NC *AC/DC 12-24 V *Receiving Range: 25 Meters *IP 44Single Swing Driveway Gate, Picket Design, 12 ft
Ship or Pick up from our showroom at #100, 11538 132A Street, Surrey, BC.
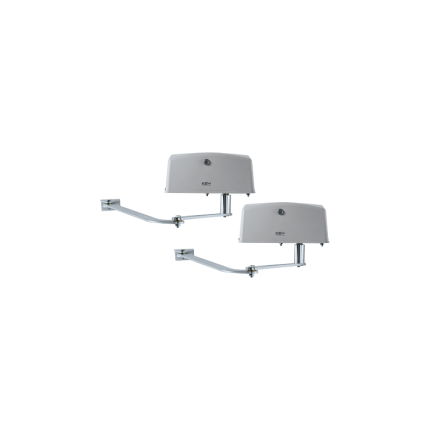
Single Swing Driveway Gate, Picket Design, 12 ft
- Aluminum Picket design single swing driveway gate
- Gate Package Includes: 1 x driveway gate panel, 2 x steel gate posts (8' H by 4" x 4" each), 2 x Heavy duty adjustable steel hinges
- Material: Aluminum Tube Framing, Aluminum pickets with a black powder paint coating
- Gate Dimensions: 12' W x 6' H.
- No hidden fees
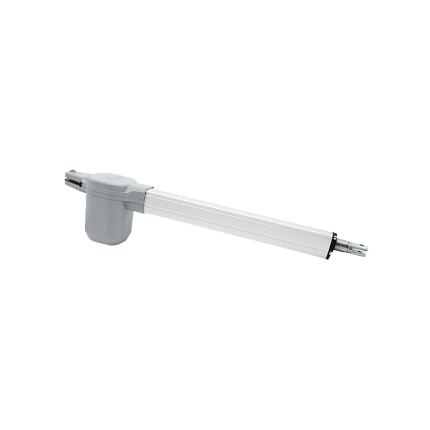
Single swing gate opener – VDS EGO24
Ship or pick up from our office.
Single swing gate opener - VDS EGO24
*Suitable gate weight: Maximum 200 Kg Included:- 1 x Electromechanical arm
- 1 x Main control board
- 1 x Waterproof box
- 2 x Remote control
- 1 x Safety sensor
- 1 x Manual release key
Single swing gate opener -Key Automation KSN5024
Ship or pick up from our office.
Product Sheet PDFSingle swing gate opener -Key Automation KSN5024
Included: *1 x Electromechanical articulated arm *1 x Main control board *2 x Remote control *1 x Manual release key *1 x Safety sensorThe Key Automation KSN5024 is a 24V DC powered articulated swing gate opener designed for single swing gates.
It is suitable for gates up to 3 meters in length and is equipped with an encoder for position feedback and safety features.
This opener is part of a line of gate automation products offered by Royal Electronics Technology Center Co..

Key Automation KSN5024
- Type: Articulated swing gate opener, meaning it uses a hinged arm to move the gate.
- Power: 24V DC.
- Encoder: Provides feedback on the gate's position, allowing for precise control and safety features.
- Gate Length: Suitable for gates up to 3 meters long.
- Applications: Designed for residential or commercial swing gates, and can be configured for inward or outward opening.
- Additional Features: Royal Electronics Technology Center Co. mentions safety photocells and key selectors as possible optional features.
Single swing gate opener -Key Automation RAY2224
Ship or pick up from our office.
Product Sheet PDFSingle swing gate opener -Key Automation RAY2224
*Suitable gate weight: Maximum 500 Kg Included: *1 x Electromechanical arm *1 x Main control board *1 x Waterproof box *2 x Remote control *1 x Set safety sensor *1 x Manual release keySingle swing gate opener -Key Automation RAY2524
Ship or pick up from our office.
Product Sheet PDFSingle swing gate opener -Key Automation RAY2524
Included: *1 x Electromechanical arm *1 x Manual release key *1 x Waterproof box *1 x Main Control Board *1 x Radio Receiver *2 x Remote Control *1 x Safety sensor *1 x KUBE *Night light systemThe Key Automation RAY2524 is a 24V DC electromechanical gear motor designed for automating swing gates, particularly for residential use.
It's suitable for gates with leaves up to 3 meters long and a maximum weight of 500kg.
The system is known for its robust construction, silent operation, and features like a night light system and easy slowdown and open limit settings.
- Type: Electromechanical gear motor.
- Power: 24V DC.
- Gate Size: Suitable for gates with leaves up to 3 meters long.
- Weight Capacity: Can handle gates weighing up to 500kg.
- Key Features:
- Robust die-cast and powder-coated aluminum body.
- Silent mechanics.
- Good duty cycle for longevity.
- Night Light system (compatible with the RAY2524).
- Easy slowdown and open limit settings.
- Water-resistant remote control.
- Robust die-cast and powder-coated aluminum body.
- Applications: Primarily for residential swing gates.
- Control System: The KUBE PRO is required for initial programming, but can be swapped for a KUBE for phone control after setup.
- Additional Features: The system also includes features like separate entrances, inputs for safety strips and photocells, and an optional battery backup input.