Diode
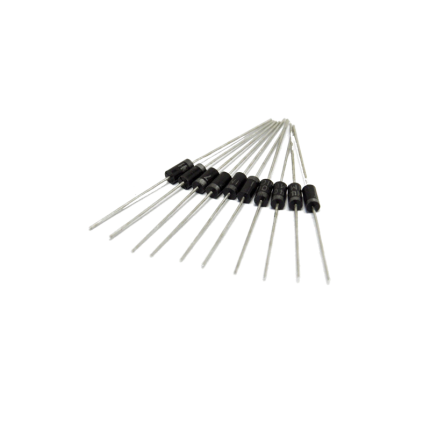
Diode 1N4007
Ship or pick up from our office.
Diode 1N4007
The 1N4007 is a very common and versatile silicon rectifier diode. It's part of the 1N400x series of general-purpose diodes, with the "7" indicating its specific voltage rating. Key Characteristics- Rectifier Diode: Its primary function is to convert alternating current (AC) into pulsating direct current (DC) by allowing current to flow in only one direction.
- High Reverse Voltage Rating: The 1N4007 can withstand a peak repetitive reverse voltage () of 1000V. This makes it suitable for high-voltage applications.
- Average Forward Current: It can handle an average forward current () of 1 Ampere (1A).
- Forward Voltage Drop: When conducting in the forward direction, it has a relatively low forward voltage drop () of approximately 0.7V to 1.1V. This voltage drop represents the power lost within the diode.
- Surge Current Capability: It can handle a non-repetitive peak surge current () of up to 30A for short durations, which is useful for handling initial power-on surges.
- Package Type: It typically comes in a DO-41 axial-lead package, which is a small, cylindrical plastic package with leads on both ends.
- Operating Temperature Range: It operates reliably over a wide temperature range, typically from -55°C to +175°C.
- Forward Bias: When a positive voltage is applied to the anode (P-side) and a negative voltage to the cathode (N-side), the diode is forward-biased. If the applied voltage exceeds the forward voltage drop (around 0.7V for silicon diodes), the diode conducts, allowing current to flow from anode to cathode.
- Reverse Bias: When a negative voltage is applied to the anode and a positive voltage to the cathode, the diode is reverse-biased. In this state, the diode acts like an open switch, blocking current flow. The 1N4007 is designed to withstand up to 1000V in this reverse-biased state before breaking down.
- Rectifier Circuits:
- Half-wave and Full-wave Rectifiers: Essential for converting AC power from the mains (like in household appliances) to DC power for electronic devices.
- Bridge Rectifiers: Used to convert the entire AC waveform into pulsating DC, achieving more efficient rectification.
- Power Supplies: Used for rectifying the AC input in power supply units to provide DC voltage to various components.
- Voltage Protection:
- Reverse Polarity Protection: Prevents damage to circuits if the power supply is connected with incorrect polarity.
- Freewheeling Diodes (Flyback Diodes): Protect sensitive components from voltage spikes generated by inductive loads (like relays, motors, and solenoids) when their magnetic field collapses.
- Voltage Spike Suppression: Helps to suppress transient voltage spikes that can occur due to switching events or lightning, safeguarding delicate electronics.
- Inverters and Converters: Used in various power conversion circuits.
- Current Flow Regulation: Can be used in simple current limiting or flow control applications.
Diode 1N5408
Ship or pick up from our office.
Diode 1N5408
The 1N5408 is a common general-purpose rectifier diode. It's designed to allow electric current to flow primarily in one direction, making it crucial for converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). Think of it like a one-way valve for electricity. It belongs to the 1N540x series of power diodes, known for their ability to handle relatively high current and voltage. Here are its key characteristics and common uses: Key Features- High Reverse Voltage Rating: It can withstand a maximum repetitive reverse voltage () of 1000V. This means it can block high voltages when current tries to flow in the "wrong" direction.
- High Forward Current Capacity: It's rated for an average rectified forward current () of 3 Amperes (A). This indicates it can handle a significant amount of current flowing through it in the correct direction.
- High Surge Current Capability: The 1N5408 can handle non-repetitive peak forward surge currents () of up to 200A for short durations, protecting circuits from sudden power spikes.
- Low Forward Voltage Drop: When conducting, it has a relatively low forward voltage drop () of approximately 1.0V to 1.2V at its rated current. A lower voltage drop means less power is lost as heat.
- Standard Recovery: It's a "standard recovery" diode, meaning its switching speed is relatively slow compared to fast recovery diodes. This makes it suitable for power rectification at lower frequencies (like 50/60 Hz AC).
- DO-201 Package: It typically comes in a DO-201 axial-leaded package, which is a through-hole component with leads extending from both ends, allowing for easy mounting on circuit boards.
- Wide Operating Temperature Range: It can operate and be stored in a wide temperature range, typically from -65°C to +175°C.
- Power Supplies and Rectifiers: This is its primary application. It efficiently converts AC input voltage into pulsating DC, which can then be smoothed by capacitors to provide a stable DC output for electronic devices. This includes full-wave and half-wave rectifier circuits.
- Battery Chargers: Used to convert AC wall power into DC for charging batteries.
- Voltage Regulation Circuits: Helps in maintaining a stable output voltage by rectifying current.
- Protection Circuits: Its ability to block reverse current makes it useful for reverse polarity protection, preventing damage to sensitive components if the power supply is connected incorrectly.
- Freewheeling Diode: Used in inductive circuits (like those with relays or motors) to provide a path for stored energy to dissipate when the current is switched off, preventing voltage spikes that could damage other components.
- Voltage Doubler Circuits: Can be used in circuits designed to effectively double the input voltage.
Diode Bridge GBU808
Ship or pick up from our office.
Diode Bridge GBU808
*8A *800V *Single Phase *Rectifier IC ChipMetal Case Diode Bridge KBPC5010
Ship or pick up from our office.
Metal Case Diode Bridge KBPC5010
The Metal Case Diode Bridge KBPC5010 is a specific type of bridge rectifier, a crucial electronic component used to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). It is widely employed in various power supply applications. Here's a breakdown of its key features and what each part of its name signifies: What is a Bridge Rectifier? A bridge rectifier is a circuit of four (or more) diodes in a specific configuration that allows for full-wave rectification. This means it efficiently converts both the positive and negative half-cycles of an AC input into a pulsating DC output. Compared to simpler half-wave rectifiers, bridge rectifiers are more efficient and provide a smoother DC output. KBPC5010 Explained- KBPC: This is typically a series designation for a family of single-phase bridge rectifiers with specific package styles.
- 50: This number indicates the maximum average forward rectified current (Io) the device can handle, which in this case is 50 Amperes (A). This high current rating makes it suitable for demanding applications.
- 10: This number typically refers to the voltage class, often indicating a maximum repetitive peak reverse voltage (VRRM) of 1000 Volts (V) (where '10' often means 10 x 100V). This high voltage rating allows it to handle substantial AC input voltages.
- Conversion: Converts single-phase AC to pulsating DC.
- Current Rating: Up to 50 Amperes (A) average forward current.
- Voltage Rating: Up to 1000 Volts (V) repetitive peak reverse voltage.
- Surge Current Capability: Often capable of handling high non-repetitive surge currents (e.g., 400A or 450A for a short duration), which is crucial for handling initial power-on transients.
- Low Forward Voltage Drop: Minimizes power loss and improves efficiency.
- High Reliability: Designed for robust performance in various environments.
- Mounting: Typically features through-hole mounting with a screw hole for chassis or heatsink mounting.
- Terminals: Often uses 0.25" (6.35 mm) Faston terminals for easy connection. Some variants (like KBPC5010W) might have wire leads.
- Operating Temperature: Wide operating junction temperature range, often from -40°C to +150°C.
- Power supplies: As a core component to rectify AC mains voltage into DC for electronic devices.
- Battery chargers: Converting AC power to DC for charging batteries.
- Motor control circuits: Providing DC power for electric motors.
- Industrial control systems: Used in various industrial applications requiring AC-to-DC conversion.
- Input rectifiers for variable frequency drives (VFDs).