Shop
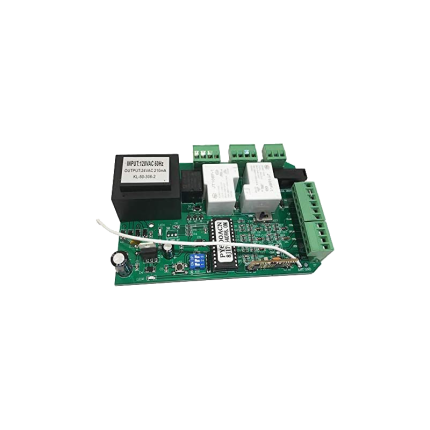
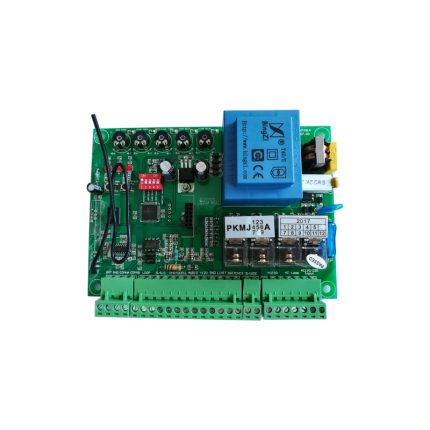
Universal sliding gate operator control board SLRG24
Ship or pick up from our office.
Universal sliding gate operator control board SLRG24
The Universal Sliding Gate Operator Control Board SLRG24 is the "brain" of an automatic sliding gate system. It's designed to be a versatile replacement or core component for various DC-powered sliding gate operators, meaning it can control a wide range of motors and integrate with different accessories. Here's a detailed look at its features and significance: Core Function of a Control Board: The control board is the central electronic unit that:- Receives Signals: Interprets commands from remote controls, keypads, safety sensors (photocells, shock sensors, loop detectors), intercom systems, and other access control devices.
- Processes Logic: Decides what action the gate should take based on the received signals and its programmed settings (e.g., open fully, partially open for pedestrian, close, stop, reverse due to obstruction).
- Activates Motor: Sends the appropriate electrical signals to the gate motor to start, stop, or reverse its movement.
- Manages Accessories: Controls the power and operation of connected safety and convenience accessories like flashing lights, electric locks, and alarm outputs.
- Universal Compatibility: This is its defining characteristic.
- DC Motor Compatibility: It's designed to work with both DC 12V and DC 24V motors. This flexibility is crucial as many sliding gate operators use one of these DC voltages. It's important to note that it is NOT compatible with AC (Alternating Current) motors (like 110V or 220V AC motors).
- Limit Switch Flexibility: It can work with both spring-type mechanical limit switches and magnetic limit switches. This is a significant advantage for a universal board, as it means it can be used with a wider range of existing gate operators.
- Input Power: The board itself typically requires an AC 24V input power. This means it likely has an internal transformer or is designed to be powered by an external AC 24V transformer.
- Full Programmability: Offers a wide range of adjustable parameters, allowing customization of gate operation to suit specific needs:
- Gate Speed: Adjustment of how fast the gate opens and closes.
- Opening/Closing Times: Setting precise durations for gate cycles.
- Automatic Closing Time: Programming a delay before the gate automatically closes after opening (e.g., 15, 30, 45 seconds, or up to 3 minutes).
- Safety Settings: Integration and management of safety sensors (photocells, obstacle detection sensitivity).
- Pedestrian Mode: Ability to set a partial opening for pedestrian access.
- Party Mode: Often allows for temporary cancellation of auto-close for periods when many visitors are expected.
- Remote Control Capability:
- Features an integrated radio receiver, typically operating at 433.92MHz with rolling code technology. Rolling code prevents unauthorized cloning of remote controls, enhancing security.
- Supports multiple remote controls (e.g., up to 20 or more), making it suitable for larger families or multi-user environments.
- Accessory Output Power: Provides DC 24V accessory output power (e.g., 200mA max) to power various external devices:
- Safety Sensors (Photocells): Connects to and powers safety beams.
- Warning Flash Lights: Powers a flashing beacon that activates when the gate is in motion.
- Keypads/Intercom Systems: Provides power and input connections for wired access control devices.
- Electric Locks: Can manage the operation of an electric lock for added security.
- Safety Mechanisms:
- Obstacle Detection: Uses current sensing or other methods to detect if the gate encounters an obstruction during movement. Upon detection, it will typically stop or reverse the gate for safety.
- Automatic Stop Function: Ensures the gate stops precisely at its programmed limits.
- Short Circuit Protection: Often includes protection for output circuits (e.g., lock output) to prevent damage from wiring faults.
- Solar System Input: The mention of "Input Solar system" suggests it's designed to be compatible with or directly connect to solar charging systems for off-grid gate installations, making it suitable for rural properties or areas without easy access to AC power.
- Installation and Durability:
- Designed for relatively easy installation.
- Built with robust components for long-lasting performance in various weather conditions, though it usually requires housing in a waterproof box (often included in a kit).
- Features an automatic power-off memory function, retaining settings after a power outage.
- Replacing a Faulty Board: If an existing 12V or 24V DC sliding gate operator has a non-functional control board, the SLRG24 could be a suitable and cost-effective replacement, reducing the need to replace the entire gate motor.
- New Custom Gate Systems: It provides a flexible "brain" for custom-built sliding gate systems where the motor and other components are chosen separately.
- Solar-Powered Gates: Its solar input capability is a definite advantage for properties in Surrey or surrounding areas that might prefer or require solar power for their gate.
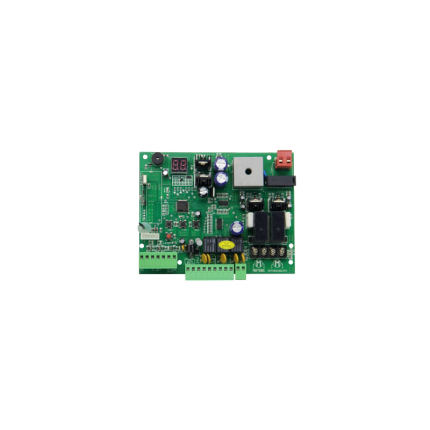
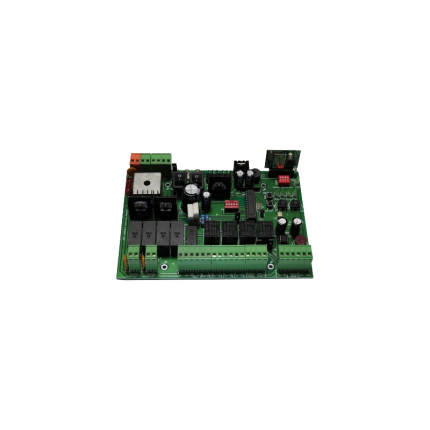
Universal Sliding gate operator’s main control board SLRG110
Universal Swing gate operator’s main control board SWRG110
Universal Swing gate operator’s main control board SWRG24
USB Gate Opener Remote
Ship or pick up from our office.
USB Gate Opener Remote
A USB gate opener remote control is a device that allows you to open and close automatic gates or garage doors by plugging a USB dongle into your car's USB port and using it as a remote.
USB Gate Opener Remote emits a sensing signal upon receiving a command from the USB port, which then triggers the gate opener to open or close the driveway gate.
Here's a more detailed explanation:
How it works:
-
USB Gate Opener Remote Dongle:The device typically includes a small USB dongle that plugs into your car's USB port.
-
Sensing Signal:When the USB is plugged in and the car is in the "on" mode, the dongle emits a sensing signal.
-
Receiver:The signal is received by a unit connected to the driveway gate motor.
-
Gate Motor Activation:The receiver then activates the gate motor, causing the driveway gate to open or close.
Key features:
-
Dual Control Modes:Some models offer both automatic and manual modes, allowing you to operate the gate either by proximity sensing or by pressing a button on the USB dongle.
-
Compact and Portable:The USB dongle is small and lightweight, making it easy to use and store in your car.
-
Easy Installation:It's designed for simple plug-and-play functionality, requiring no complex setup.
-
Replacement Accessory:The USB gate opener remote serves as a convenient replacement for traditional gate remote controls.
USB Gate Operator Remote
USB Gate Operator Remote
A USB gate operator remote control is a device that allows you to open and close automatic gates or garage doors by plugging a USB dongle into your car's USB port and using it as a remote. USB Gate Operator Remote emits a sensing signal upon receiving a command from the USB port, which then triggers the gate opener to open or close the driveway gate. Here's a more detailed explanation: -How it works: USB Dongle: The device typically includes a small USB dongle that plugs into your car's USB port. Sensing Signal: When the USB is plugged in and the car is in the "on" mode, the dongle emits a sensing signal. Receiver: The signal is received by a unit connected to the driveway gate motor. Gate Motor Activation: The receiver then activates the gate motor, causing the driveway gate to open or close. -Key features: Dual Control Modes: Some models offer both automatic and manual modes, allowing you to operate the gate either by proximity sensing or by pressing a button on the USB dongle. Compact and Portable: The USB dongle is small and lightweight, making it easy to use and store in your car. Easy Installation: It's designed for simple plug-and-play functionality, requiring no complex setup. Replacement Accessory: It serves as a convenient replacement for traditional gate remote controls.Vehicle alarm ultrasonic sensor
Ship or pick up from our office.
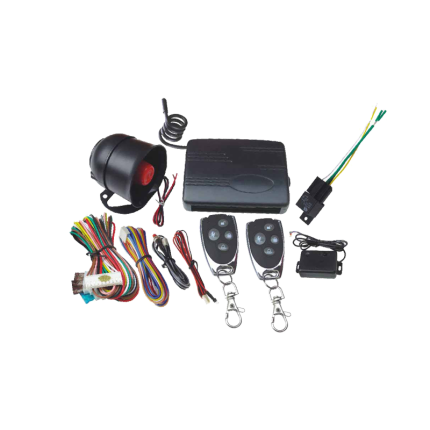
Vehicle alarm ultrasonic sensor
A vehicle alarm ultrasonic sensor is a type of motion sensor used in car alarm systems to detect movement within the interior of a vehicle when the alarm is armed. It's designed to provide an extra layer of security by catching intruders who might try to gain access by breaking a window or otherwise entering the cabin without opening a door. Here's how it generally works:- Emission of Ultrasonic Waves: When the car alarm system is armed, the ultrasonic sensor (or typically a pair of sensors, one on each side of the front of the vehicle, often mounted on the A-pillars) emits high-frequency sound waves. These sound waves are beyond the range of human hearing, hence "ultrasonic." These waves fill the interior space of the vehicle.
- Monitoring for Echoes: The sensor continuously monitors the echoes of these sound waves as they bounce off the surfaces within the car's cabin (seats, dashboard, windows, roof, etc.). This creates a consistent pattern of reflected waves.
- Detection of Disturbance: If an intruder enters the vehicle, or if there's any significant movement within the cabin (e.g., someone reaches in through a broken window, or a pet is left inside and moves around), this movement disrupts the established pattern of the ultrasonic waves. The sound waves bounce back differently, indicating a change in the air pressure or the environment within the car.
- Alarm Trigger: When the sensor detects this disturbance or change in the reflected wave pattern, it signals the car's alarm system. The alarm then triggers, typically sounding the horn, flashing the lights, and in some cases, activating a dedicated siren.
- Interior Protection: Its primary purpose is to detect intrusion into the passenger compartment, complementing other sensors like door, hood, and trunk sensors.
- Invisible Barrier: It creates an "invisible" protective barrier within the vehicle's cabin.
- Sensitivity: Ultrasonic sensors are quite sensitive and can detect even minor movements, which makes them effective against various forms of unauthorized entry.
- False Alarm Reduction: Quality ultrasonic sensors are designed to minimize false alarms. However, factors like leaving windows open, a sunroof ajar, or having pets or large insects inside the car can sometimes trigger them.
- Compatibility: They are often integrated into factory-installed alarm systems in newer vehicles, but can also be added as aftermarket components to enhance existing security systems.
- Adjustable Sensitivity: Many systems allow for adjustment of the sensor's sensitivity to tailor its performance to different environments or situations.
- Not for Convertibles: Due to their reliance on enclosed air space and reflected sound waves, ultrasonic sensors are generally not suitable for convertibles or vehicles with soft tops, as the open or flexible roof would not properly reflect the sound waves, leading to false alarms or ineffective monitoring.
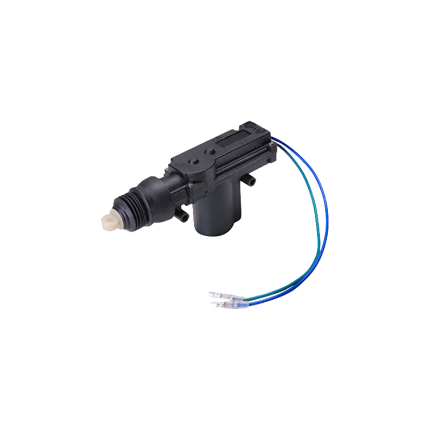
Vehicle central door lock actuator
Ship or pick up from our office.
Vehicle central door lock actuator
A vehicle central door lock actuator is the electromechanical component responsible for physically locking and unlocking your car's doors when you press a button on your key fob, the interior door switch, or when the central locking system otherwise activates (e.g., speed-sensitive locking). Think of it as the "muscle" of your car's power door locks. Here's a more detailed breakdown: How it Works:- Signal Transmission: When you press the lock or unlock button on your key fob (remote control) or the switch inside the car, a radio frequency signal or an electrical signal is sent to the vehicle's Electronic Control Unit (ECU), often referred to as the Body Control Module (BCM).
- Processing by ECU: The ECU decodes this signal and determines whether the command is to lock or unlock the doors.
- Actuator Activation: The ECU then sends an electrical current to the door lock actuator located inside each door.
- Mechanical Movement: The actuator contains a small electric motor, a set of gears, and linkages (or sometimes a cable).
- When the motor receives the electrical current, it rotates in one direction to engage the locking mechanism (locking the door) or in the opposite direction to disengage it (unlocking the door).
- The gears amplify the motor's force, and the linkages convert the rotational motion of the motor into the linear or pivotal motion needed to move the door latch and lock/unlock the door.
- Feedback (Optional): Some systems provide feedback, such as a light flash or a horn chirp, to confirm that the doors have been locked or unlocked.
- Electric Motor: A small, reversible DC motor that provides the power.
- Gear Train: A series of gears that transmit and multiply the motor's torque to move the locking mechanism.
- Linkages/Cable: Connect the internal mechanism of the actuator to the door's actual latching mechanism.
- Electrical Contacts/Switches: These are inside the actuator and tell the ECU the current state of the lock (locked or unlocked).
- Housing: Encapsulates and protects all the internal components.
- Motor-driven Actuators (Most Common in Modern Cars): As described above, these use a small electric motor and gears. They offer precise control and are generally durable.
- Solenoid-driven Actuators (Older or Simpler Systems): These use an electromagnetic coil (solenoid) to create a rapid, linear pulling or pushing motion. They are typically simpler but can be less robust for frequent use.
- Convenience: Allows for simultaneous locking or unlocking of all doors with a single action, eliminating the need to manually lock each door.
- Security: Ensures all doors are properly locked, preventing unauthorized access.
- Safety: Modern systems often include features like:
- Speed-sensitive locking: Doors automatically lock when the vehicle reaches a certain speed.
- Automatic re-locking: If you unlock the car but don't open a door within a certain time, the doors will re-lock automatically.
- Anti-theft features: Some systems disable interior release levers when "double locked" to prevent entry even after glass breakage.
- Remote Keyless Entry: Integral to the operation of key fob remotes.
- Inconsistent Locking/Unlocking: One or more doors don't respond reliably to the lock/unlock command from the fob or interior switch.
- Unusual Noises: Clicking, grinding, buzzing, or whirring sounds coming from inside the door when trying to lock or unlock. This often indicates worn gears or a struggling motor.
- Sluggish Operation: The door lock moves slowly or with a delay.
- Door Stays Locked or Unlocked: A specific door might be stuck in the locked or unlocked position, even when the rest of the car responds. You might still be able to operate it manually.
- Random Locking/Unlocking: The door might lock or unlock itself without input.
- "Door Ajar" Warning Light: In some cases, a faulty actuator (specifically, a worn internal switch) can cause the "door open" warning light to stay on even when the door is closed, or trigger the car alarm.
Vehicle HID light kit
Ship or pick up from our office.
Vehicle HID light kit
A vehicle HID (High-Intensity Discharge) light kit is an aftermarket product designed to convert a vehicle's standard halogen headlights to HID lighting. HID lights, also known as Xenon lights, produce light by igniting noble gases (like xenon) within a sealed bulb using an electric arc, rather than by heating a filament like traditional halogen bulbs. Components of a Typical HID Light Kit: A complete HID light kit generally consists of the following key components for each headlight:- HID Bulbs: These are the actual light sources. Unlike halogen bulbs, they don't have a filament. Instead, they contain xenon gas and metal salts. They come in various bulb sizes (e.g., H1, H7, 9006, D2S) to match the original halogen bulb fitment of a vehicle's headlight housing. They also come in different "color temperatures" measured in Kelvin (K), ranging from yellow-white (around 3000K-4300K) to pure white (5000K-6000K) and blue-white (8000K+).
- Ballasts (Igniters/Power Converters): This is the most crucial part of an HID kit. Halogen bulbs operate on 12V DC, but HID bulbs require a very high voltage (tens of thousands of volts) to ignite the gas and then a stable, lower voltage (around 85V AC) to keep the arc sustained. The ballast performs this function:
- Ignition: It provides the initial high-voltage pulse to ignite the xenon gas.
- Regulation: Once ignited, it regulates the current and voltage to the bulb to maintain a stable arc and optimal light output.
- Canbus Ballasts: Many modern vehicles use a "CAN bus" (Controller Area Network) system that monitors electrical circuits. If the vehicle detects a lower power draw from HID bulbs compared to original halogens, it might throw a "bulb out" error or cause flickering. "Canbus ballasts" are designed to mimic the electrical load of halogen bulbs to prevent these errors.
- Wiring Harness (Optional but Recommended): In some cases, particularly for vehicles with sensitive electrical systems or DRLs (Daytime Running Lights) that operate at reduced voltage, a relay wiring harness is used. This harness draws direct power from the battery, ensuring the ballasts receive consistent 12-14V, with the original headlight wiring acting only as a trigger.
- Capacitors/Resistors (Optional): These may be included or sold separately to address specific vehicle electrical issues like flickering (capacitors) or "bulb out" warnings (resistors), especially in vehicles with pulse width modulation (PWM) in their headlight circuits.
- Brightness (Lumen Output): HID lights are significantly brighter than standard halogen bulbs, offering more light output on the road.
- Color Temperature: Many users prefer the whiter or bluer light of HIDs, which often looks more modern and can improve visibility of road signs.
- Energy Efficiency: While brighter, HIDs can sometimes be more energy-efficient than halogens for the amount of light they produce.
- Lifespan: HID bulbs generally have a longer lifespan than halogen bulbs, though ballasts can fail.
- Glare and Light Distribution: Halogen headlight housings (reflectors or projectors) are precisely engineered to work with the light-emitting point and light distribution pattern of a halogen filament. When an HID bulb (which has a different light source and emits light differently) is placed in a housing designed for halogen, it creates an uncontrolled and often excessive amount of glare. This can blind oncoming drivers, creating a significant safety hazard.
- BC Motor Vehicle Act Regulations (Section 4.02 & 4.04): These regulations generally state that vehicle lamps must comply with original manufacturer specifications and approved standards (like SAE) and must not cause undue glare or dazzle oncoming traffic. Specifically, if a headlight housing is marked for a Halogen (HR) bulb, it is unlawful to put an HID (HG) light source in it.
- DOT/SAE Compliance: Aftermarket HID conversion kits typically do not meet DOT (Department of Transportation) or SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) standards for the entire headlight assembly when installed in a halogen housing. Only complete headlight assemblies that are factory-designed for HIDs and meet these standards are truly legal.
- Enforcement in BC/Canada: While enforcement can vary, police in BC and across Canada can issue tickets (e.g., a $110 fine under the Highway Traffic Act) and potentially even order vehicles off the road for non-compliant lighting that causes excessive glare. They often look for vehicles with "uncontrolled" light output, especially if it's causing complaints.
- Best Practice: Projector Retrofits: To legally and safely upgrade to HID lighting, the proper method is a "retrofit." This involves replacing the entire headlight housing (or at least the internal projector lens assembly) with one specifically designed for HID bulbs. This ensures the light is properly focused and distributed, preventing glare. However, this is a more complex and expensive process than simply installing a "kit."